Anti Spam reviews in App store
Back to the 1980s, the NLP systems still based on complex sets of hand-written rules. These rules become hard to maintain since it grows exponential depend on the length of sentences. Moreover, new words pop up every day so we also have to maintain the old roles before developing any new one. Most important, we can’t use these rules on other languages since the rules are languages-specify.
With the power of the modern computer, we tried machine learning algorithms like decision trees to replace some of the hand-written rules. As we gain more and more data, we start using statistical models like hidden markov models to predict the probability of the word depends on the input data. Nowadays, with the help from the deep neural network, word embeddings help us to convert a word from higher dimension space to a lower one.
Spam reviews problem
The spam reviews problem in China’s app store is serious. With my observation, more than 40% of customer reviews are not helpful. most of them just random words, spam, ads, unrelated contents or mean reviews which didn’t help users or the application itself. I don’t know why Apple choose to ignore this problem since the ranking of the app mostly depends on its rankings. We can also find other similar problems like amazon fake reviews or Taobao fake reviews.
Problem Statement
I try to solve a general problem, how to find useful reviews and how to detect spam or fake reviews. This problem also exists in other country’s app store, but since China is a big market, so it looks more obvious. In this project, I’m going to use hybrid algorithms to detect the useful reviews.
Datasets and Inputs
The datasets contain 13000 customer reviews from the Apple review API,
each data point includes a username, rankings, title, and review.
The customer reviews come from top 5 free applications from 6 different categories in China’s app store. Each application includes 400 data points, 200 of them from most recent reviews and the left from most helpful reviews. I labeled all the customer reviews as useful or useless.
Solution Statement
In this section, I want to discuss what kind of reviews should be considered useless.
The review is too short
When a review is too short, It didn’t provide enough information for the user. For instance, reviews like these didn’t help, because they didn’t provide the reason why they like or hate the application.
"喜欢" (I like it)
"不错" (Nice app)
"下载用不了"(Can't use it after downloaded)
Even though this review was written by a real user, but we choose to ignore it.
The review is too long
Usually, users would not take too much time to read a single review. Second, If you look at the most useful reviews display by Apple, you would found most of them are a super long sentence (more than 200 words) which means Apple use the length of reviews to identify the quality of the reviews heavily. Unfortunately, spammer also noticed this. A spammer can type in lots of random words and a 5-star ranking to let an application gets a better score. Example below
“比寂寞更多的人和人和事情的不同在于不懂你说话了??不会有一个人说你会让孩子更坚强……不知道是不是真的没有办法了?我们可以接受现实生活”(Random words)
Grammatical errors
Sometimes the review has lots of grammatical errors so the user doesn’t understand what the review means. We can calculate the probability of the part of speech from the review by using POS transition matrix. In the meantime, we can also solve random words problem with this algorithm.
Ads
Ads about gambling are everywhere, we can use Bayes algorithm to detect these ads.
Benchmark Model
Since we use several algorithms here, I choose to benchmark the model by comparing the final hybrid algorithms with the one only use POS transition matrix or Bayes algorithm.
Evaluation Metrics
F1 score, Accuracy score, Precision score, Recall score to be used to quantify the performance of the model
Project Design
Data collection
I collected all the data from the Apple Review API,https://itunes.apple.com/cn/rss/customerreviews/id={0}/sortBy=mostRecent/page={1}/jsonData label
I labeled 13000 reviews by myself. After that, I did a little trick here.
for all reviews, I calculated their Jaccard similarity between each other. If some of the reviews have more than 80% similarity. (At the end of the project, I found I can use SVD to speed up the process.) I assume that both of them are spam review, then mark both of them as useless.
Detection
Random guess
The first method is a random guess, we guess all the review is useful.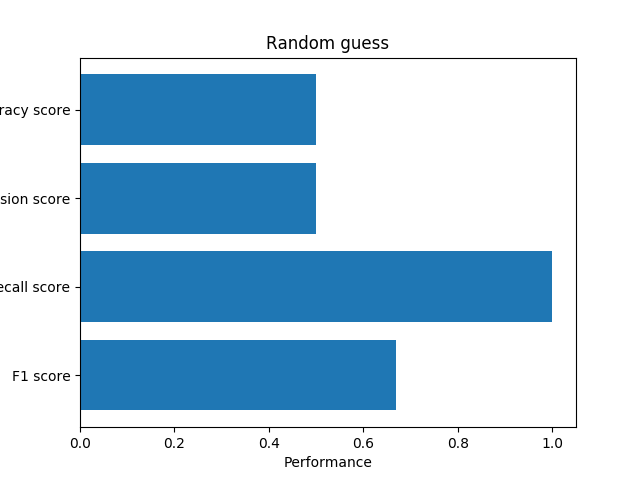
The review is too short or too long
Here is the distribution for the sentence length of useful reviews.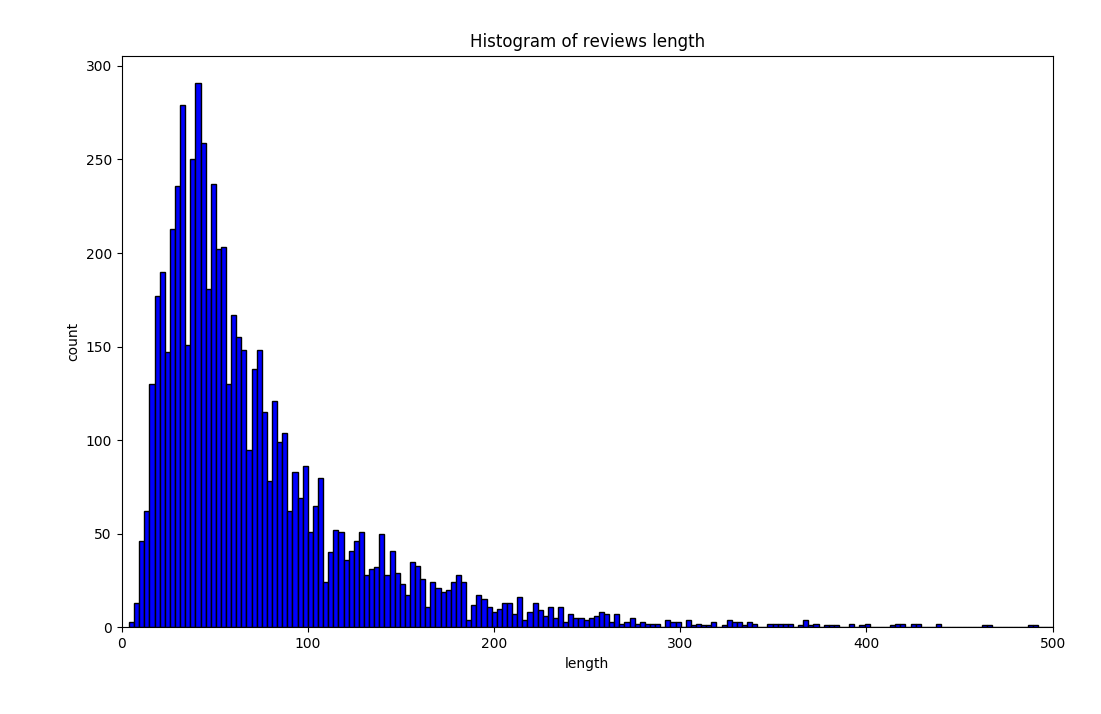
And the distribution for the sentence length of useless reviews.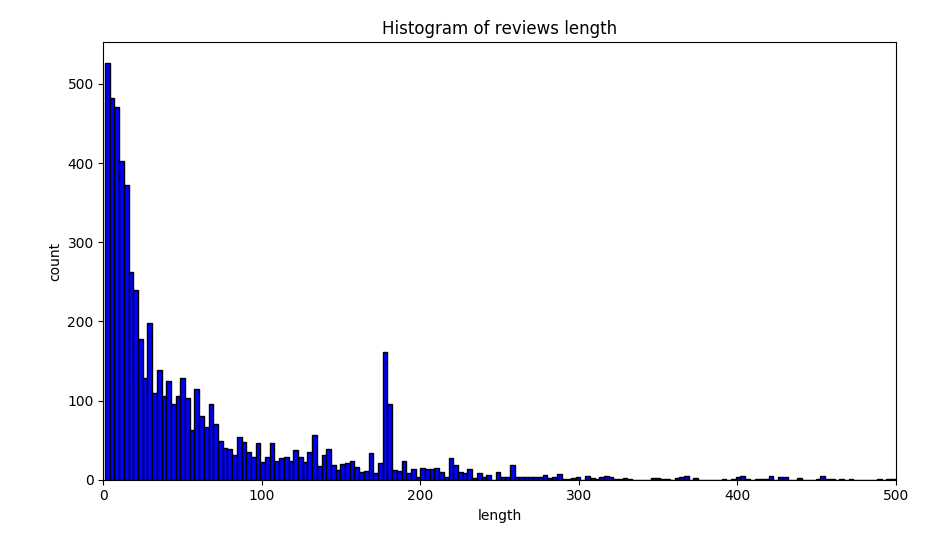
After calculation, I found that 99.5% of the length of the useful reviews are between (10, 465). So I set the reviews out of the range to be useless.
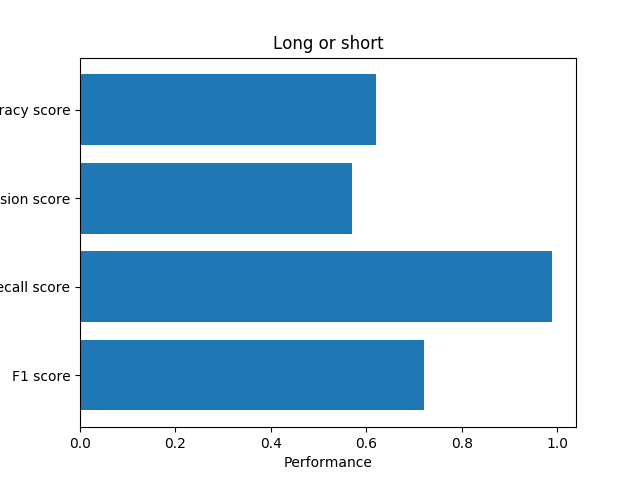
Grammar problem
I use a POS matrix which contains the transition probability between all kind of POS. For instance, the probability from adj to n is 10%. I calculated the probability after tokenizer the review. If it is too small then what expected, we mark this review has grammatical errors. Here is the distribution for useful and useless reviews.
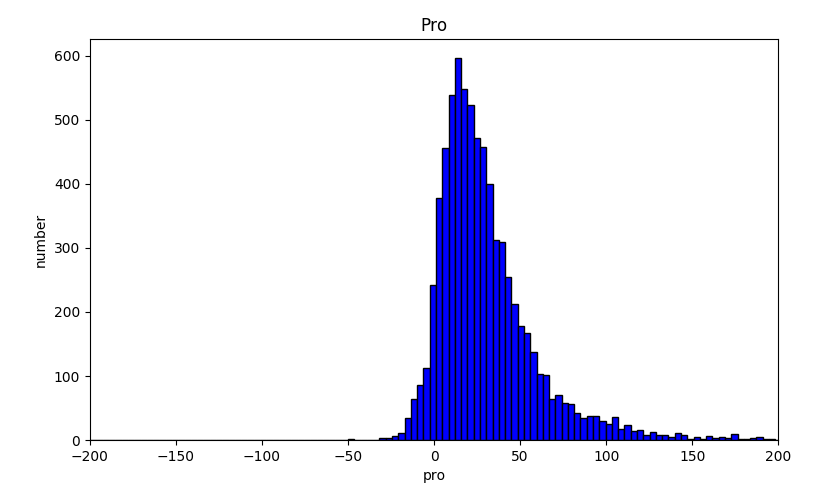
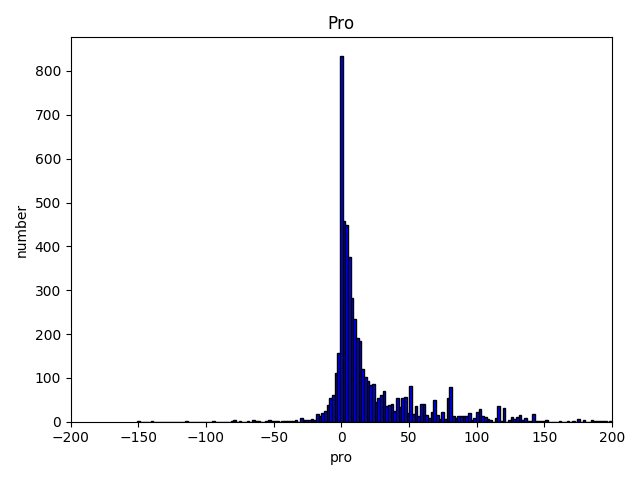
Unfortunately, when I labeled the reviews I only labeled useful and useless instead of useful, useless, grammatical errors, ads so this method didn’t help at all. But if we correctly labeled the reviews, I’m sure we can benefit from it.
Ads
We use Naive Bayes to detect ads, we use pkuseg to tokenizer and MultinomialNB in sklearn.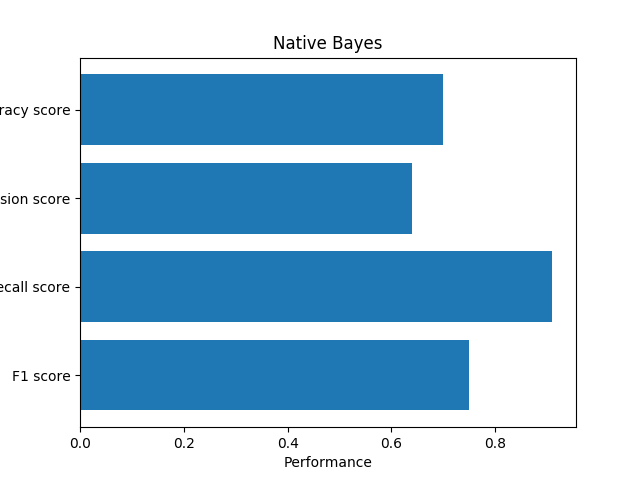
Combine all of them
If we use multiple algorithms together, we can get a better result.
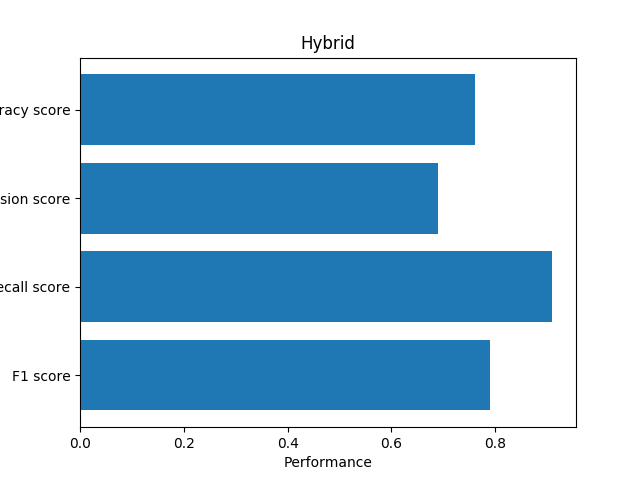
Conclusion
Base on our current implementation, we helped Apple detected
There are lots of other methods to detect useless reviews.